Temperature Definition - Understanding The Science Of Heat And Cold
When you think about temperature, what comes to mind? The weather forecast? How warm or cool your coffee feels? Or perhaps the way your body reacts to a chilly room? The concept of temperature is something we interact with daily, yet its scientific meaning often remains a bit mysterious. At its core, temperature is a measure of how hot or cold something is, but it’s much more than just that. It’s a physical property that affects everything from weather patterns to how our bodies function. In this article, we’ll explore the temperature definition in a way that’s easy to grasp and relatable to everyday experiences.
Temperature is one of those terms that gets thrown around a lot, but its true meaning often gets lost in translation. From the weather outside to the heat in your kitchen, temperature plays a role in nearly everything. It’s not just about feeling comfortable or uncomfortable—it’s about understanding how energy moves and how it impacts the world around us. Whether you’re checking the thermometer on a frosty morning or adjusting the oven for dinner, temperature is the key to making sense of it all.
So why is temperature so important? Beyond just telling us whether to wear a jacket or grab an ice pack, it’s a fundamental concept in physics that helps explain how energy flows and how substances behave. From the smallest particles to the largest systems, temperature is the thread that ties everything together. As we delve deeper into its definition, you’ll discover how it connects to everything from cooking to climate change. Let’s take a closer look at what temperature really means and why it matters.
What Is Temperature Definition All About?
At its most basic level, temperature is a way to describe how hot or cold something feels. But scientifically speaking, it’s much more than just a sensation—it’s a measurable property. Temperature measures the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. In other words, it tells us how much the tiny bits that make up matter are moving around. The faster they move, the higher the temperature. This concept might sound simple, but it’s what allows us to understand and predict so many things in the world around us.
Now, here’s a little history lesson. The word “temperature” comes from the Latin term “temperare,” which means to mix or restrain. Over time, the meaning shifted from describing a balance or mix to becoming a term for heat or cold. By the late 1600s, the modern sense of temperature had taken shape, and we started using tools like thermometers to measure it. So, in a way, temperature is a concept that’s evolved alongside human understanding of the physical world.
How Do We Measure Temperature Definition?
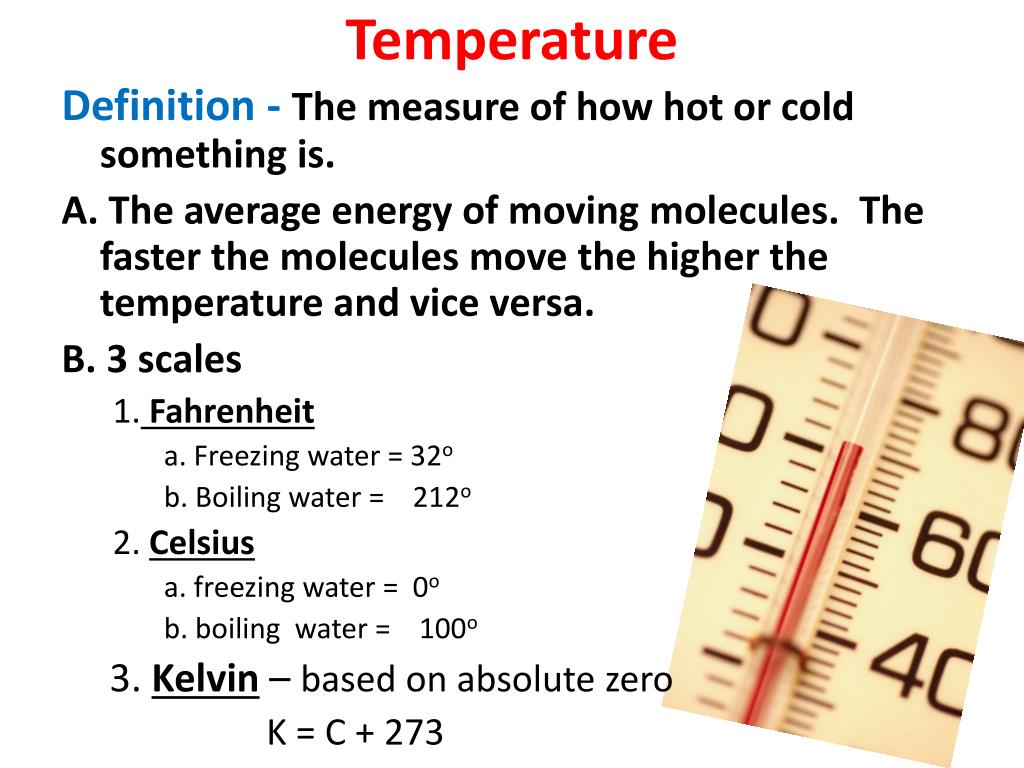
Measuring temperature is all about finding a standard way to compare how hot or cold something is. That’s where temperature scales come in. There are three main ones used today: Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. Celsius is the most common, especially in countries using the metric system. It’s based on the freezing and boiling points of water, making it pretty straightforward to understand. Fahrenheit, on the other hand, is a bit more complicated but still widely used, especially in the United States. Kelvin, the scientific standard, starts at absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature where particles stop moving entirely.
But why do we need different scales? Well, it’s kind of like using different units for distance—miles, kilometers, or feet. Each scale has its own context and purpose. For example, scientists prefer Kelvin because it makes calculations easier, while weather forecasters often stick to Celsius or Fahrenheit because it’s what people are used to. Anyway, the key point is that these scales give us a way to quantify temperature in a consistent way.
Why Is Temperature Definition Important?
Temperature isn’t just a number on a thermometer—it’s a vital piece of information that affects everything from the food we eat to the air we breathe. In fact, it’s one of the fundamental concepts in physics. Without it, we wouldn’t be able to explain things like heat transfer, weather patterns, or even how our bodies regulate internal heat. Think about it: when you feel feverish, your body is telling you that something’s off with your internal temperature. Or when you cook a steak, you’re relying on temperature to get the perfect doneness. So, in a way, temperature is the unsung hero of our daily lives.
Let’s talk about heat transfer for a moment. Temperature determines the direction that heat moves. Heat always flows from a warmer object to a cooler one. That’s why, if you touch a hot stove, the heat transfers to your hand, making it painful. It’s also why ice melts when you leave it out in the sun—the heat from the air moves into the ice, warming it up. This basic principle is what drives so many processes in nature, from the weather to the way engines work.
What Are the Different Temperature Scales?
So, we’ve already mentioned Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin, but what makes them different? Each scale has its own starting point and increments, which can make conversions a bit tricky. For example, water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius but 32 degrees Fahrenheit. Boiling water is 100 degrees Celsius but a whopping 212 degrees Fahrenheit. Kelvin, being a scientific scale, starts at absolute zero, which is -273.15 degrees Celsius. It’s all a bit confusing, but once you get the hang of it, it’s not so bad.
In some respects, the choice of scale depends on the situation. Scientists love Kelvin because it’s precise and easy to work with in equations. Everyday folks tend to prefer Celsius or Fahrenheit because they’re more familiar. But regardless of which scale you use, the idea behind temperature stays the same—it’s about measuring how much energy is being transferred between particles. Honestly, it’s kind of fascinating how such a simple concept can have so many different applications.
How Does Temperature Affect Our Daily Lives?
Temperature affects nearly every aspect of our daily lives, even if we don’t always notice it. For instance, the weather is all about temperature. Whether it’s a scorching summer day or a frigid winter morning, temperature determines how we dress, how we plan our activities, and even how we feel. Beyond the weather, temperature also plays a huge role in cooking. Baking bread, frying eggs, or roasting vegetables—all of these processes rely on getting the temperature just right. And let’s not forget about our bodies. Human beings have an internal temperature that needs to stay within a pretty narrow range to function properly. If it gets too high or too low, things can go seriously wrong.
Temperature also impacts the world around us in ways we might not always think about. For example, it affects how plants grow, how animals behave, and even how buildings are designed. Architects have to consider temperature when planning insulation, heating, and cooling systems. Similarly, farmers need to understand temperature patterns to know when to plant and harvest crops. In short, temperature is a key factor in just about everything we do, whether we realize it or not.
Can Temperature Be Negative?
Now, here’s a fun question—can temperature actually be negative? Well, sort of. On the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, temperatures below zero are considered negative. But on the Kelvin scale, there’s no such thing as negative temperature because it starts at absolute zero, the point where particles stop moving altogether. So, in a way, negative temperatures only exist because of the way we define our scales. It’s kind of like saying you owe someone negative money—it’s all relative to the system you’re using.
Interestingly, scientists have discovered some weird phenomena where systems can appear to have negative temperatures. These situations are pretty rare and usually involve quantum mechanics, but they do exist. Anyway, the point is that temperature isn’t always as straightforward as it seems. Sometimes, it can get a little complicated, but that’s part of what makes it so interesting to study.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Temperature?
Even though temperature is such a common concept, there are still a lot of misconceptions floating around. One big one is that temperature and heat are the same thing. They’re related, sure, but they’re not the same. Temperature measures the average kinetic energy of particles, while heat is the actual transfer of energy between objects. Another common misconception is that colder temperatures always mean slower movement. While that’s usually true, there are exceptions, especially in extreme conditions like superfluids or Bose-Einstein condensates.
People also sometimes confuse temperature with thermal comfort. Just because a room is a certain temperature doesn’t mean it feels comfortable. Factors like humidity, air movement, and even clothing can affect how warm or cool we feel. So, while temperature is a great starting point, it’s not the whole story when it comes to how we experience heat and cold. Anyway, these are just a few examples of how temperature can be misunderstood, but with a little more knowledge, it’s easy to clear things up.
How Is Temperature Related to Energy?
Temperature is all about energy—specifically, the energy of motion in particles. The more energy particles have, the faster they move, and the higher the temperature. This relationship is why temperature is so important in physics and other sciences. It’s a way to quantify the energy in a system and predict how it will behave. For example, when you heat up water, you’re adding energy to the system, which makes the water molecules move faster. Eventually, they move so fast that they turn into steam, which is why boiling happens.
Energy transfer is another big part of the temperature story. When you touch a cold object, heat energy flows from your hand to the object, cooling your hand down. Similarly, when you sit near a fire, the heat energy radiates toward you, warming you up. These processes happen because of temperature differences, and they’re what keep the world running smoothly. Anyway, the bottom line is that temperature and energy are deeply connected, and understanding one helps you understand the other.
What Does the Future Hold for Temperature Studies?
As our understanding of the universe grows, so does our knowledge of temperature. Scientists are constantly exploring new ways to measure and manipulate temperature, especially in extreme conditions. For example, researchers are working on ways to create and study systems at temperatures close to absolute zero. These experiments could lead to breakthroughs in quantum computing and other advanced technologies. Meanwhile, climate scientists are using temperature data to better understand global warming and its effects on the planet. So, in a way, temperature research is more important now than ever before.
Finally, let’s talk about why all this matters. Understanding temperature isn’t just about satisfying curiosity—it’s about improving our lives and the world around us. Whether it’s designing better insulation for homes, developing new materials for electronics, or finding ways to combat climate change, temperature plays a key role. As we continue to learn more, the possibilities seem almost endless. Anyway, that’s the beauty of science—there’s always something new to discover.
Summary
Temperature is more than just a number on a thermometer—it’s a fundamental concept that shapes our world. From its origins in Latin to its modern-day applications, temperature has evolved into a powerful tool for understanding how energy moves and how substances behave. By learning about temperature scales, misconceptions, and its relationship to energy, we can gain a deeper appreciation for this essential property. Whether you’re checking the weather, cooking dinner, or exploring the mysteries of the universe, temperature is always there, quietly influencing everything around us.
Table of Contents
- What Is Temperature Definition All About?
- How Do We Measure Temperature Definition?
- Why Is Temperature Definition Important?
- What Are the Different Temperature Scales?
- How Does Temperature Affect Our Daily Lives?
- Can Temperature Be Negative?
- What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Temperature?
- What Does the Future Hold for Temperature Studies?

What Is Temperature? Definition in Science
PPT - Temperature PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:3736268

What Is Absolute Temperature? Definition and Scales