Kosher Definition - What Does It Mean And Why Is It Important
When you hear the word "kosher," you might think it's just about food, but there's a whole lot more to it than that. In Jewish tradition, kosher refers to foods that are fit for consumption according to the dietary laws found in the Torah. These rules have been around for centuries and continue to guide what people eat and how they prepare meals. Kosher isn't just about what's on your plate; it’s a way of life for many.
For those unfamiliar, the term kosher comes from the Hebrew word "kasher," meaning "fit" or "proper." It’s not just about avoiding certain foods, but also about how food is prepared, cooked, and served. In fact, the concept extends beyond food to include items like ritual objects and even practices. As you explore the basics of kosher living, you'll find it’s a system rich in tradition and meaning.
Understanding kosher isn’t just for those practicing Judaism. With more people interested in ethical eating, kosher certification has become a trusted standard for food quality and cleanliness. Whether you're looking to follow a kosher diet or simply curious about the customs, there’s a lot to discover. Let’s take a closer look at what makes something kosher and why it matters.
- Mountain Climber William Stampfl
- Four Seasons Orlando Baby
- Hilde Osland
- Seven Sirius Benjamin
- James Callis
What Exactly Does Kosher Definition Cover?
So, what exactly does the term kosher encompass? At its core, kosher refers to foods that are acceptable under Jewish dietary laws. These laws, or kashrut, determine which animals can be eaten, how they must be slaughtered, and how food should be prepared. For instance, kosher meats come from animals that chew the cud and have split hooves, like cows and sheep. Fish must have fins and scales to qualify. Meanwhile, certain birds are considered kosher, while others are off-limits.
Is All Food Automatically Kosher?
Not all food is kosher, and the rules can get pretty specific. For example, meat and dairy products can’t be mixed in kosher cooking. This means no cheeseburgers or cream sauces on steak if you're following a kosher diet. Additionally, the equipment used to prepare kosher food must also be kosher. This ensures there’s no cross-contamination with non-kosher items. It’s all about keeping things pure and aligned with religious guidelines.
For example, if you buy meat at a kosher butcher, the process starts with ensuring the animal was slaughtered in a humane and kosher manner. The meat is then salted to remove blood, as consuming blood is prohibited. This attention to detail extends to every step of food preparation, making it a bit like following a recipe book written by generations of rabbis.
Where Does the Kosher Definition Come From?
Alright, let’s talk about where these rules come from. The origins of kosher laws trace back to the Hebrew Bible, specifically in the books of Leviticus and Deuteronomy. Over time, rabbis expanded on these ancient texts, creating a detailed framework for what constitutes kosher food. This system wasn’t developed overnight; it evolved over centuries, with input from religious scholars and leaders. Today, kosher certification agencies help ensure that food meets these standards, giving consumers peace of mind.
So, in some respects, the kosher definition is like a map for what’s permissible and what’s not. It’s not just about the food itself but also about the process. The idea is to create a connection between what you eat and your spiritual well-being. It’s a holistic approach to eating that emphasizes mindfulness and intentionality.
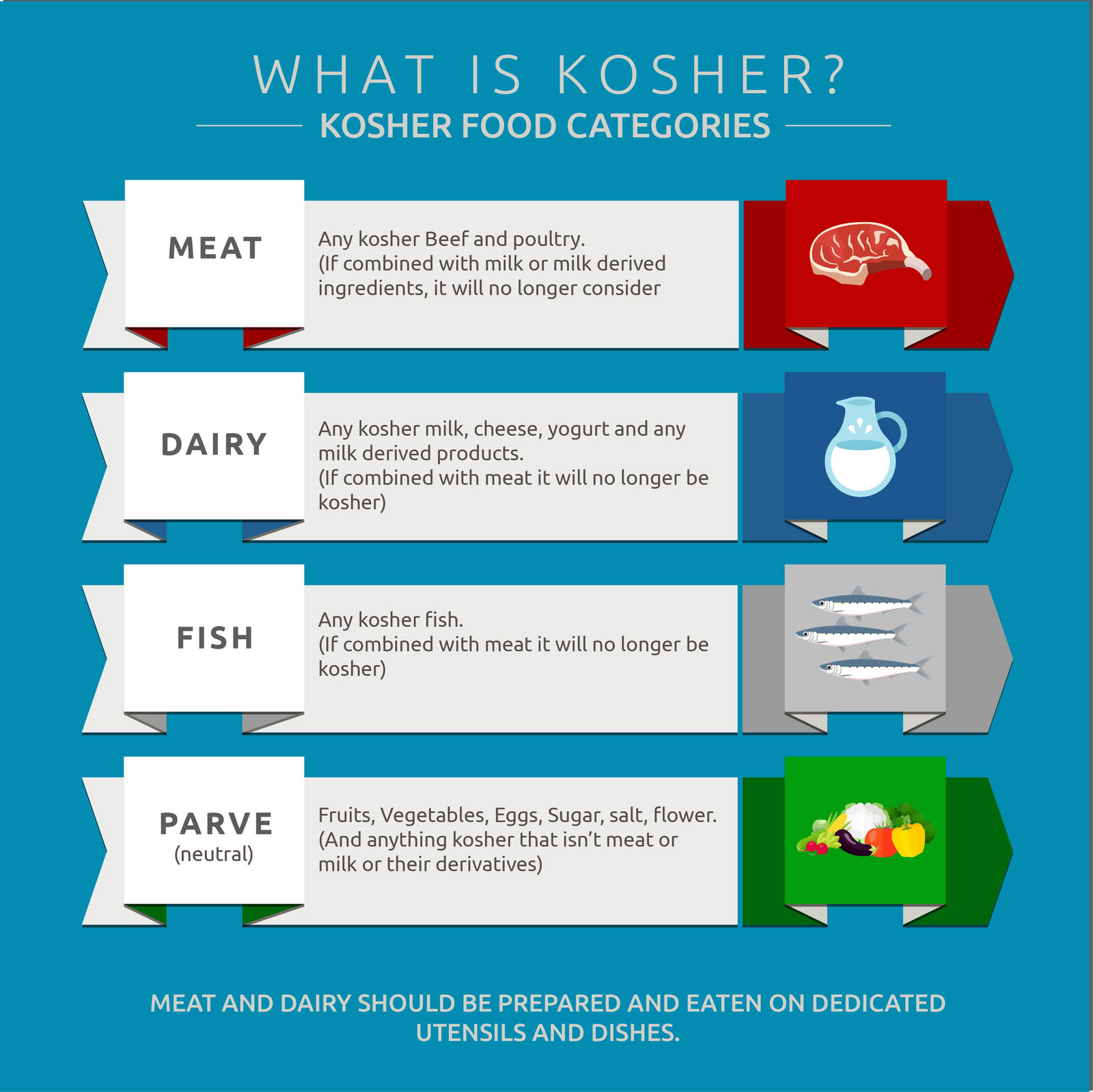
What Are the Three Main Categories of Kosher Food?
Kosher foods are usually grouped into three main categories: meat, dairy, and pareve. Meat includes beef, lamb, and poultry, while dairy covers milk, cheese, and yogurt. Pareve refers to foods that are neither meat nor dairy, like fruits, vegetables, grains, and eggs. This categorization helps people keep track of what they can and can’t eat together. For instance, you wouldn’t serve a cheese plate alongside a steak dinner in a kosher home.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Meat: Animals that chew the cud and have split hooves, like cows and sheep.
- Dairy: Milk, cheese, and other milk-based products from kosher animals.
- Pareve: Foods that aren’t meat or dairy, including fruits, vegetables, and grains.
These categories aren’t just about what you eat but also about how you prepare and serve food. For example, separate utensils and cookware are often used for meat and dairy dishes to avoid mixing the two.
How Does the Kosher Definition Apply to Passover?
Now, let’s touch on Passover, a significant holiday in Jewish tradition. During Passover, the kosher definition gets even stricter. Leavened bread, known as chametz, is forbidden, and people eat matzah instead. This change reflects the story of the Exodus, when the Israelites fled Egypt in such a hurry that their bread didn’t have time to rise. To honor this, kosher for Passover foods must meet additional criteria, ensuring they’re free from chametz.
For those observing Passover, it’s not just about avoiding certain foods but also about cleaning and preparing the home. Many people will have a separate set of dishes and cookware specifically for Passover meals. It’s a way of fully immersing in the holiday and its meaning.
What Makes a Food Non-Kosher?
So, what makes a food non-kosher? Well, it could be a number of things. For one, if an animal doesn’t meet the criteria—like pigs, which don’t have split hooves—it’s automatically off-limits. Similarly, if the animal wasn’t slaughtered according to kosher guidelines, the meat wouldn’t be considered kosher. Even if the ingredients are kosher, cross-contamination during preparation can disqualify a dish.
For instance, if a chef uses the same pan to cook chicken and then boils milk in it without proper cleaning, the milk would no longer be kosher. It’s all about maintaining those boundaries and ensuring everything stays pure. This is why kosher certification is so important. It gives people confidence that the food they’re buying meets these standards.
Why Is Kosher Certification Important?
Nowadays, kosher certification has become a big deal, even for people who aren’t Jewish. It’s a way of ensuring food quality and cleanliness, which appeals to a wide range of consumers. When you see a kosher certification symbol on a product, it means that a rabbinic agency has inspected the ingredients and production process to ensure everything is kosher. This adds an extra layer of trust and reliability.
For businesses, getting kosher certification can open up new markets and increase sales. Many people, regardless of religion, prefer kosher products because they’re seen as cleaner and more ethically produced. It’s like a stamp of approval that tells consumers the food meets high standards. Plus, with more people paying attention to what they eat, kosher certification can be a real selling point.
How Do You Know If Something Is Kosher?
So, how do you tell if something is kosher? The easiest way is to look for a kosher certification symbol on the packaging. These symbols, often called hechsher marks, indicate that the product has been approved by a kosher certification agency. Different agencies use different symbols, so it’s good to familiarize yourself with them if you’re shopping for kosher foods.
Of course, if you’re cooking at home, you’ll need to ensure all your ingredients and equipment are kosher. This might mean buying separate sets of pots and pans for meat and dairy dishes or carefully checking ingredient lists for hidden non-kosher items. It takes a bit of effort, but many find it worth it for the peace of mind it brings.
What Does Kosher Definition Mean Beyond Food?
Finally, let’s talk about how the kosher definition extends beyond food. In Jewish tradition, the word kosher can apply to other things, like ritual objects and even actions. For example, a Torah scroll or a mikvah (ritual bath) might be described as kosher if it meets specific requirements. In modern usage, the term has also come to mean anything that’s proper or legitimate, even outside of religious contexts.
So, in a way, kosher is more than just a set of dietary rules. It’s a way of thinking about the world and the choices we make. Whether you’re following a kosher diet or simply appreciating the principles behind it, there’s a lot to learn and explore. It’s a tradition that connects people to their faith, their community, and their values.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Does Kosher Definition Cover?
- Is All Food Automatically Kosher?
- Where Does the Kosher Definition Come From?
- What Are the Three Main Categories of Kosher Food?
- How Does the Kosher Definition Apply to Passover?
- What Makes a Food Non-Kosher?
- Why Is Kosher Certification Important?
- How Do You Know If Something Is Kosher?
- What Does Kosher Definition Mean Beyond Food?
Summary of the Article's Contents
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the concept of kosher and what it means in both religious and everyday contexts. From the origins of kosher laws in the Hebrew Bible to the modern-day importance of kosher certification, there’s a lot to unpack. We’ve looked at the three main categories of kosher food—meat, dairy, and pareve—and how they interact. Additionally, we’ve discussed the stricter rules during Passover and the significance of kosher certification in today’s market.
Understanding the kosher definition goes beyond just knowing which foods are allowed. It’s about connecting with a rich tradition and making mindful choices about what we consume. Whether you’re following a kosher diet or simply curious about the customs, there’s always more to learn. So, grab a kosher snack and keep exploring!

Kosher Cooking: What Makes Food Kosher | Taste of Home
Tamm - What Is Kosher? - Page 1 - Created with Publitas.com

Kosher Products