Organelle Definition - Understanding The Little Organs In Cells
Cells, the building blocks of life, are fascinating structures with many parts working together to keep living things alive. Among these parts are organelles, which act like the body's organs but on a much smaller scale. These little organs inside cells are crucial for various tasks, such as producing energy, storing nutrients, and even helping cells reproduce. Without organelles, cells wouldn't be able to function properly, and life as we know it wouldn't exist.
Just like our bodies need different organs to perform various jobs, cells rely on organelles to handle specific tasks. For instance, the nucleus acts as the control center, while mitochondria are responsible for energy production. These structures are often surrounded by a protective layer called a membrane, allowing them to carry out their functions without interference from other parts of the cell. Understanding these tiny but powerful components helps us appreciate how cells maintain life.
Learning about organelles is not just for scientists or biology enthusiasts. It's a topic that affects everyone because it explains the basics of how life works at the cellular level. From plants producing their food through photosynthesis to animals breaking down nutrients for energy, organelles play a key role in these processes. So, if you've ever wondered what makes cells tick, exploring the world of organelles might be just what you're looking for.
What Exactly Are Organelles?
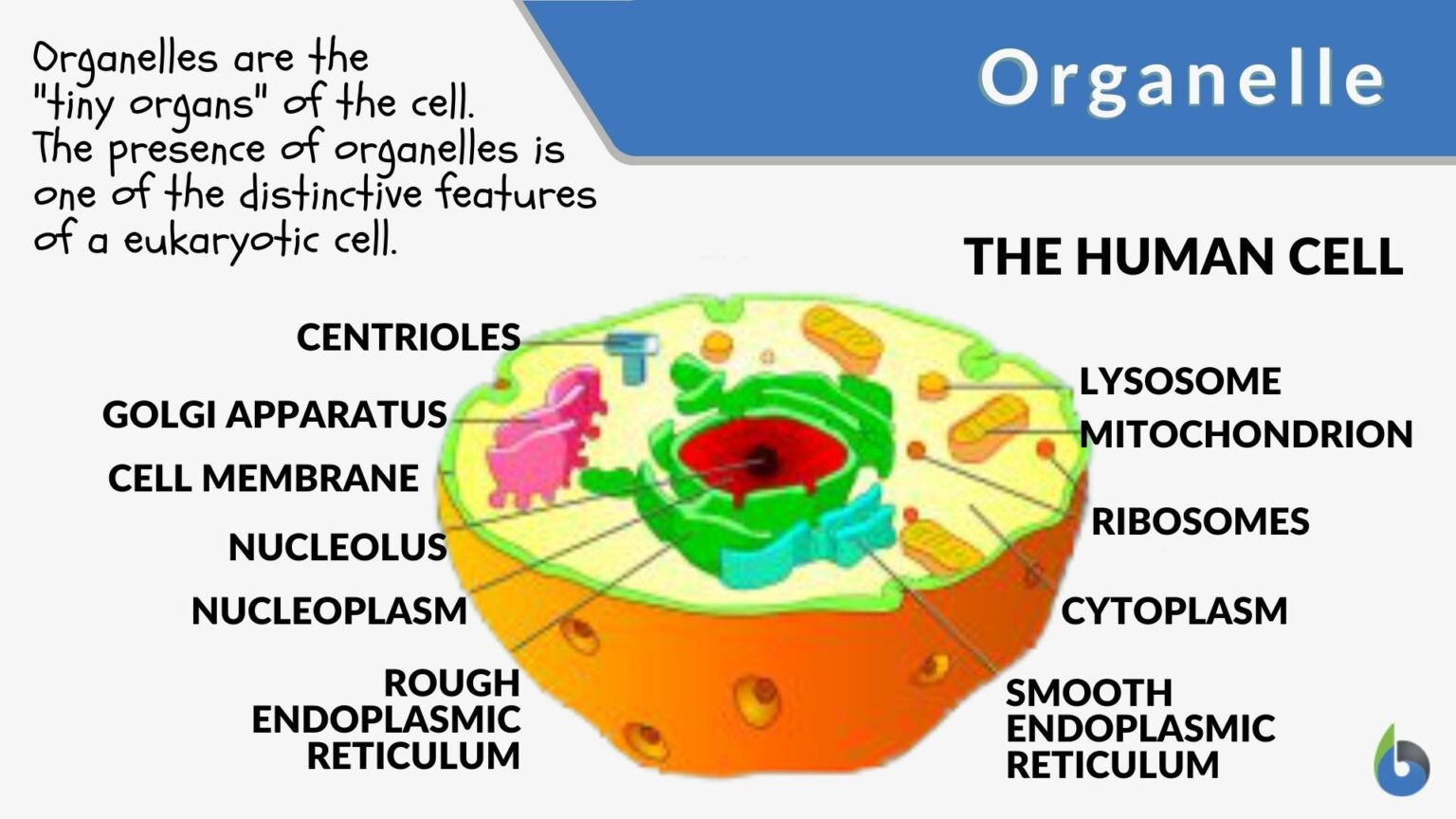
Organelles are like the tiny machines inside cells that help them function. The word organelle actually means "little organs," which gives you a pretty good idea of what they do. Just as our bodies have organs to keep us alive, cells have organelles to do the same. They each have their own job, whether it's storing things, making energy, or helping the cell grow.
For example, the nucleus, often called the control center of the cell, holds all the genetic information. Then there's the mitochondria, which is often referred to as the powerhouse because it makes energy for the cell. These little structures are separated from the rest of the cell by a membrane, which helps them focus on their tasks without getting mixed up with other things happening in the cell.
What Are the Common Types of Organelles?
Some of the most well-known organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, and chloroplasts. Each of these has its own special job. The nucleus stores the DNA, which is like the blueprint for the cell. The mitochondria, as mentioned before, make energy. Ribosomes are little factories that build proteins, which are essential for cell function. Chloroplasts, found in plant cells, help with photosynthesis, the process where plants make their own food using sunlight.
- Sagacious Meaning
- Brookie Recipe
- Straight Hair Haircuts For Guys
- I Understand It Now Meme
- Cambio De Horario Usa
How Do Organelles Function in Cells?
Every organelle has its own way of doing things. For instance, the mitochondria break down sugar to produce energy, which the cell can then use to do its job. Ribosomes read the instructions from the nucleus and build proteins based on those instructions. Meanwhile, chloroplasts in plant cells capture sunlight and use it to turn carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen, which is how plants make their own food.
What Is the Organelle Definition?
The organelle definition is pretty straightforward. An organelle is a small structure within a cell that performs a specific task. They are kind of like the body's organs but on a much smaller scale. These structures are usually surrounded by a membrane, which helps them stay focused on their job. Some organelles, like the nucleus, are found in nearly all cells, while others, like chloroplasts, are only found in certain types of cells.
Cells need organelles to function properly. Without them, cells wouldn't be able to do things like make energy, store nutrients, or even reproduce. Each organelle has its own role to play, and they all work together to keep the cell alive and healthy. Understanding how organelles function can help us understand how life works at the cellular level.
Why Is the Organelle Definition Important?
Knowing the organelle definition is important because it helps us understand how cells work. Cells are the basic units of life, and organelles are the parts that make them function. By studying organelles, scientists can learn more about how living things grow, develop, and stay healthy. This knowledge can lead to new treatments for diseases and a better understanding of how life works.
What Makes Organelles Unique Compared to Other Cell Structures?
Organelles are unique because they are specialized structures with specific jobs. Unlike other parts of the cell, such as the cytoplasm or cell membrane, organelles are usually surrounded by a membrane, which helps them stay focused on their task. This allows them to perform their functions without interference from other parts of the cell. Additionally, some organelles, like mitochondria and chloroplasts, have their own DNA, which makes them even more unique.
What Are the Differences Between Plant and Animal Cell Organelles?
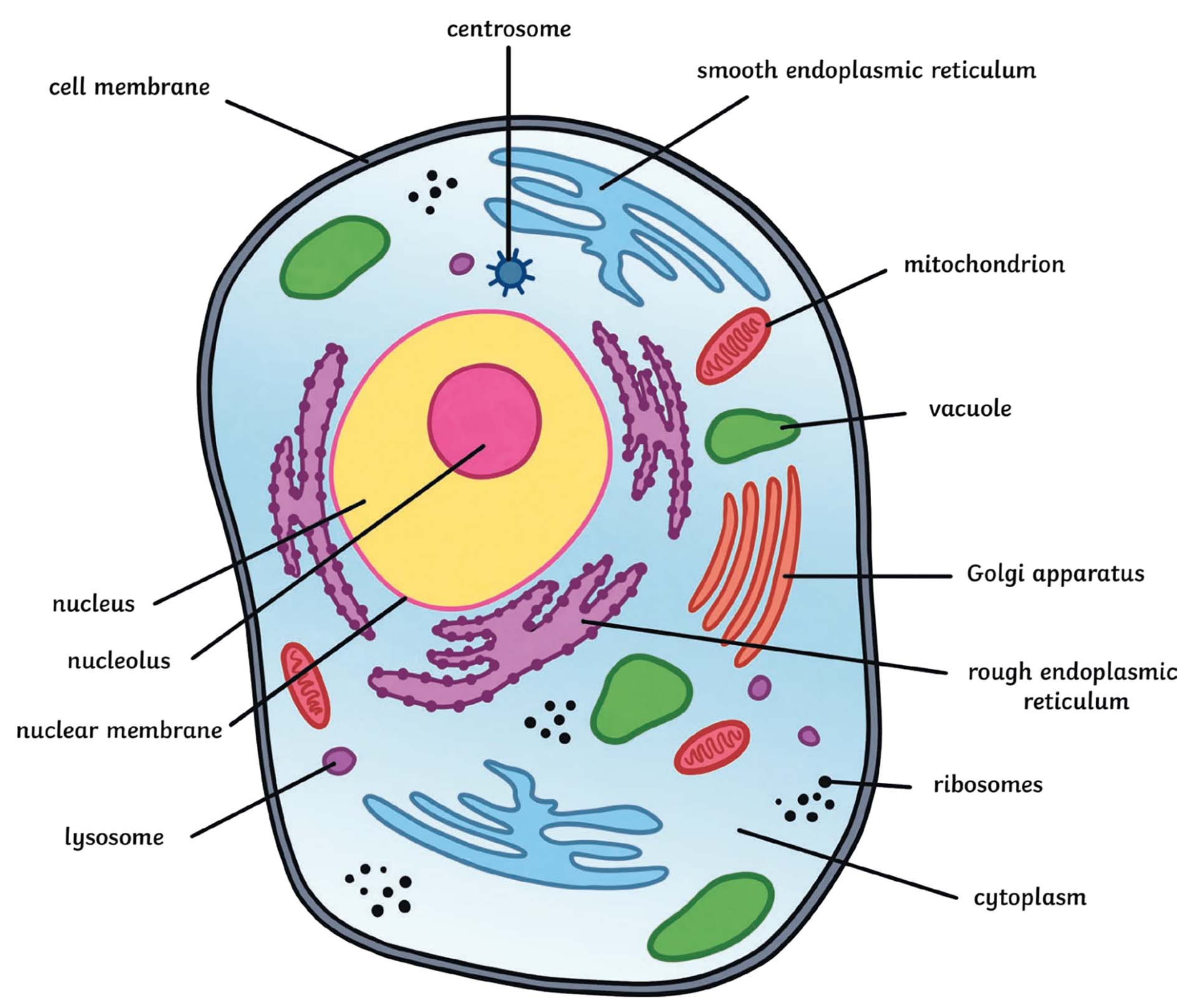
Plant and animal cells have some organelles in common, such as the nucleus and mitochondria, but they also have some differences. For example, plant cells have chloroplasts, which help them make their own food through photosynthesis. Animal cells don't have chloroplasts because they get their food from other sources. Additionally, plant cells have a cell wall, which provides extra support and protection, while animal cells have a more flexible cell membrane.
These differences reflect the different needs of plants and animals. Plants need to make their own food, so they have chloroplasts to help with that. Animals, on the other hand, need to be able to move and change shape, so they have a more flexible cell membrane. Understanding these differences can help us appreciate how diverse life can be at the cellular level.
How Are Organelles Classified in Organelle Definition?
Organelles can be classified based on their structure and function. For example, some organelles, like the nucleus and mitochondria, are surrounded by a double membrane, while others, like ribosomes, are not surrounded by a membrane at all. Additionally, some organelles, like chloroplasts, are only found in certain types of cells, while others, like the nucleus, are found in nearly all cells.
This classification helps scientists understand how organelles work and how they relate to each other. By studying the structure and function of organelles, scientists can learn more about how cells function and how life works at the cellular level. This knowledge can lead to new discoveries and a better understanding of the world around us.
What Are Some Examples of Organelles in Organelle Definition?
Some common examples of organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, and chloroplasts. Each of these has its own special job. The nucleus stores the DNA, which is like the blueprint for the cell. The mitochondria make energy for the cell. Ribosomes build proteins, which are essential for cell function. Chloroplasts, found in plant cells, help with photosynthesis, the process where plants make their own food using sunlight.
There are many other organelles too, each with its own unique function. By studying these structures, scientists can learn more about how cells work and how life functions at the most basic level. Understanding organelles is key to understanding life itself.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Are Organelles?
- What Are the Common Types of Organelles?
- How Do Organelles Function in Cells?
- What Is the Organelle Definition?
- Why Is the Organelle Definition Important?
- What Makes Organelles Unique Compared to Other Cell Structures?
- What Are the Differences Between Plant and Animal Cell Organelles?
- How Are Organelles Classified in Organelle Definition?
Organelles are fascinating little structures that help cells function. They each have their own job, whether it's storing DNA, making energy, building proteins, or helping with photosynthesis. By understanding how organelles work, we can gain a better appreciation for how life functions at the cellular level. So, the next time you hear the word organelle, remember that these tiny structures are the backbone of life as we know it.
Organelle - Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary

Organelle Definition
What is an Animal Cell? | Definition and Functions | Twinkl