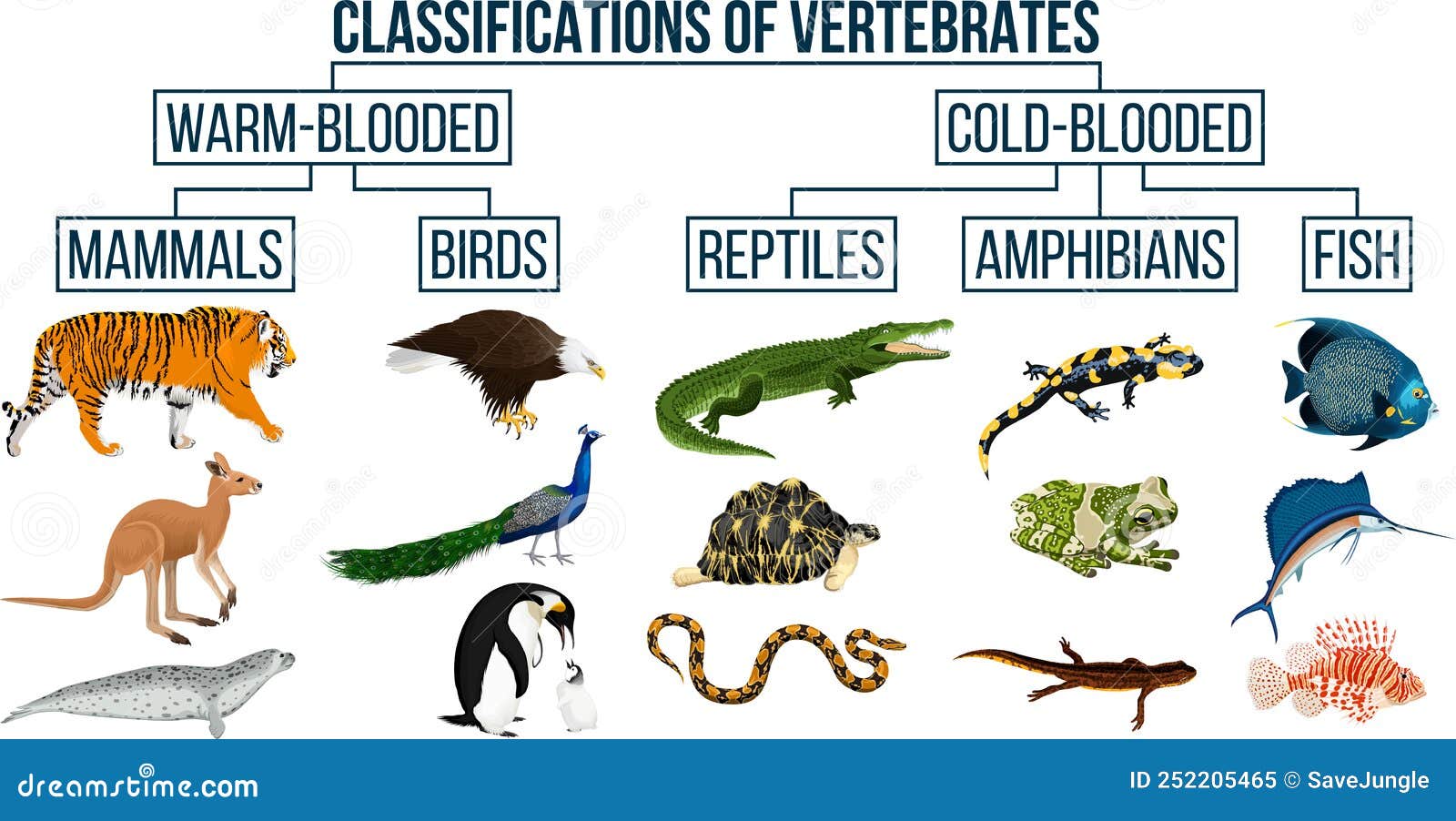
Are Birds Reptiles - Exploring The Connection Between Feathers And Scales
Have you ever wondered why birds share so many traits with reptiles? It turns out, the connection between these two groups of animals is deeper than you might think. Birds, those creatures flitting about in the sky, are not just related to dinosaurs—they actually are dinosaurs. This revelation stems from the way scientists classify organisms based on genetic similarity. In this article, we'll explore how birds fit into the reptile family tree and why they’re considered part of the same group.
But wait, there’s more. Birds are closely related to crocodiles, which come from a group called archosaurs. This means that the evolutionary path of birds and reptiles intertwined long before birds took to the skies. Understanding this connection helps us see how birds evolved from small, feathered dinosaurs and how their traits align with reptiles.
So, are birds reptiles? Yes, according to some systems of classification. They share features like laying eggs and excreting waste as uric acid. Yet, birds have their own unique characteristics, such as feathers and specialized reproductive systems. Let’s take a closer look at what makes birds so closely related to reptiles and why this classification matters.
Table of Contents
- Are Birds Reptiles - The Basics
- How Did Birds Evolve from Dinosaurs?
- What Traits Do Birds Share with Reptiles?
- Why Do Birds Lay Eggs Like Reptiles?
- Do Birds and Reptiles Have Similar Reproductive Systems?
- How Are Birds Closely Related to Crocodiles?
- What Does Genetic Evidence Tell Us About Birds and Reptiles?
- Why Do Some People Say Birds Aren’t Reptiles?
Are Birds Reptiles - The Basics
So, let’s start with the basics. Birds are technically classified as reptiles under certain systems. This classification comes from the way scientists group animals based on shared ancestry. Birds evolved from dinosaurs, and dinosaurs are reptiles, so it makes sense that birds would be part of the reptile family. In fact, birds share a common ancestor with snakes, lizards, and crocodiles. This shared history means they have a lot in common, even if they look quite different now.
How Did Birds Evolve from Dinosaurs?
Alright, so here’s the story. Birds didn’t just pop up out of nowhere. They evolved from small, feathered dinosaurs that lived during the late Jurassic period. These dinosaurs began growing feathers, which eventually helped them take flight. Over time, these feathered dinosaurs developed into the birds we see today. So, when we say birds are dinosaurs, we’re not exaggerating—it’s a fact backed by fossil evidence.
For example, theropod dinosaurs, which are the ancestors of birds, share over 100 traits with modern birds. Some of these traits include a fused collarbone, which we call a wishbone. This connection shows just how closely related birds are to their dinosaur ancestors. It’s almost like looking at a family tree, where birds and dinosaurs share a common branch.
What Traits Do Birds Share with Reptiles?
Now, let’s talk about the traits birds and reptiles share. One big one is how they handle waste. Both birds and reptiles excrete nitrogenous waste as uric acid. This is different from mammals, which excrete waste as urea. Birds also don’t have a urinary bladder or external urethral opening, which is more like reptiles than mammals.
In some respects, birds and reptiles are quite similar. For example, they both lay eggs. Birds, though, tend to build nests and incubate their eggs by sitting on them. Reptiles, on the other hand, often rely on camouflage to protect their eggs. This difference in behavior shows how birds have adapted to their environment in unique ways.
Why Do Birds Lay Eggs Like Reptiles?
That’s a good question. Birds lay eggs because they inherited this trait from their reptilian ancestors. The amniotic egg, which has a membrane enclosing the developing embryo, is a feature shared by both groups. This adaptation allowed animals to reproduce on land without needing water, which was a big deal in evolutionary terms.
So, while birds have developed some unique features, like feathers and flight, they still retain this ancient trait of laying eggs. It’s kind of like keeping one foot in the past while moving forward. This connection to their reptilian roots is just another piece of the puzzle when it comes to understanding birds.
Do Birds and Reptiles Have Similar Reproductive Systems?
Well, sort of. Birds and reptiles both lay eggs, but their reproductive systems differ in some key ways. For instance, most birds have only one functional ovary, while reptiles typically have two. Fertilization is also different. In birds, fertilization happens internally, while in reptiles, it often happens externally. These differences show how birds have evolved to suit their specific needs.
Still, the similarities are there. Both groups lay eggs, and both have adapted to their environments in ways that help them survive. Birds, for example, build nests and care for their young, which is a behavior not commonly seen in reptiles. This nurturing behavior is one of the things that makes birds unique, even if they share a common ancestry with reptiles.
How Are Birds Closely Related to Crocodiles?
Here’s a fun fact. Birds are most closely related to crocodiles, which are part of a group called archosaurs. This means that birds and crocodiles share a common ancestor that lived millions of years ago. This connection is why birds are considered part of the reptile family tree.
Think about it this way. Crocodiles and birds both come from the same branch of the evolutionary tree. They share features like laying eggs and excreting waste as uric acid. Yet, they’ve evolved in different directions, with birds taking to the skies and crocodiles sticking to the water. It’s like cousins who grew up in different parts of the world but still share a family resemblance.
What Does Genetic Evidence Tell Us About Birds and Reptiles?
Genetic evidence plays a big role in understanding how birds and reptiles are related. By studying the DNA of these animals, scientists can see how closely they’re related. This evidence shows that birds and reptiles share a common ancestor, which means they’re part of the same family tree.
For example, genetic studies have shown that birds evolved from theropod dinosaurs, which are a type of reptile. This connection is backed up by fossil evidence, which shows how birds developed from small, feathered dinosaurs. It’s a bit like putting together a puzzle, where each piece of evidence helps us see the bigger picture.
Why Do Some People Say Birds Aren’t Reptiles?
That’s a fair question. Some people argue that birds aren’t reptiles because they have unique traits, like feathers and flight. While it’s true that birds have evolved in ways that make them different from other reptiles, they still share a common ancestry. This means they’re technically part of the reptile family, even if they’ve developed their own unique characteristics.
In some ways, it’s like saying a dog isn’t a mammal because it has fur and barks. Sure, dogs have their own unique traits, but they’re still mammals. Similarly, birds have their own unique traits, but they’re still reptiles. It’s all about how we classify animals based on their shared ancestry.
Final Summary
So, are birds reptiles? The answer is yes, according to the way scientists classify animals. Birds evolved from dinosaurs, which are reptiles, and share a common ancestor with snakes, lizards, and crocodiles. They have traits like laying eggs and excreting waste as uric acid, which they inherited from their reptilian ancestors. Yet, birds have also developed their own unique features, like feathers and flight, which set them apart from other reptiles.
Understanding this connection helps us see how birds fit into the bigger picture of life on Earth. It’s a reminder that even the most seemingly different creatures can share a common history. So, the next time you see a bird flying overhead, remember that it’s not just a bird—it’s also a reptile.

Reptiles: The Ultimate Guide - All You Need To Know About Reptiles

Birds and Reptile Relation – Clyde Peeling's Reptiland
Classification Of Vertebrates Animals. Mammals, Birds, Reptiles