What What Is Energy - A Comprehensive Guide To Its Forms And Functions
Energy plays a vital role in our day-to-day existence. Whether it’s the fuel that powers our cars or the electricity that lights up our homes, energy is everywhere. But what exactly is energy? Put simply, it’s the ability to do work, and it comes in many different forms. From the food we eat to the sun shining above us, energy is the driving force behind everything we do. Understanding its various forms and functions can help us appreciate its importance in our lives.
Energy isn’t something we can touch or see directly, but we experience its effects all the time. For instance, when you eat a sandwich, your body converts the chemical energy stored in the food into the energy needed to move, think, and function. Similarly, when you flip a switch, electrical energy flows through wires to power your devices. Energy is a concept that transcends boundaries, connecting the smallest particles to the largest galaxies.
As we delve deeper into what energy is, it becomes clear that its forms and transformations shape the world around us. From potential energy stored in objects at rest to kinetic energy in motion, each type plays a unique role. Whether you're curious about how energy works or how it impacts daily life, this article aims to shed light on its fascinating nature. So, let’s get started!
What What is Energy - The Basics
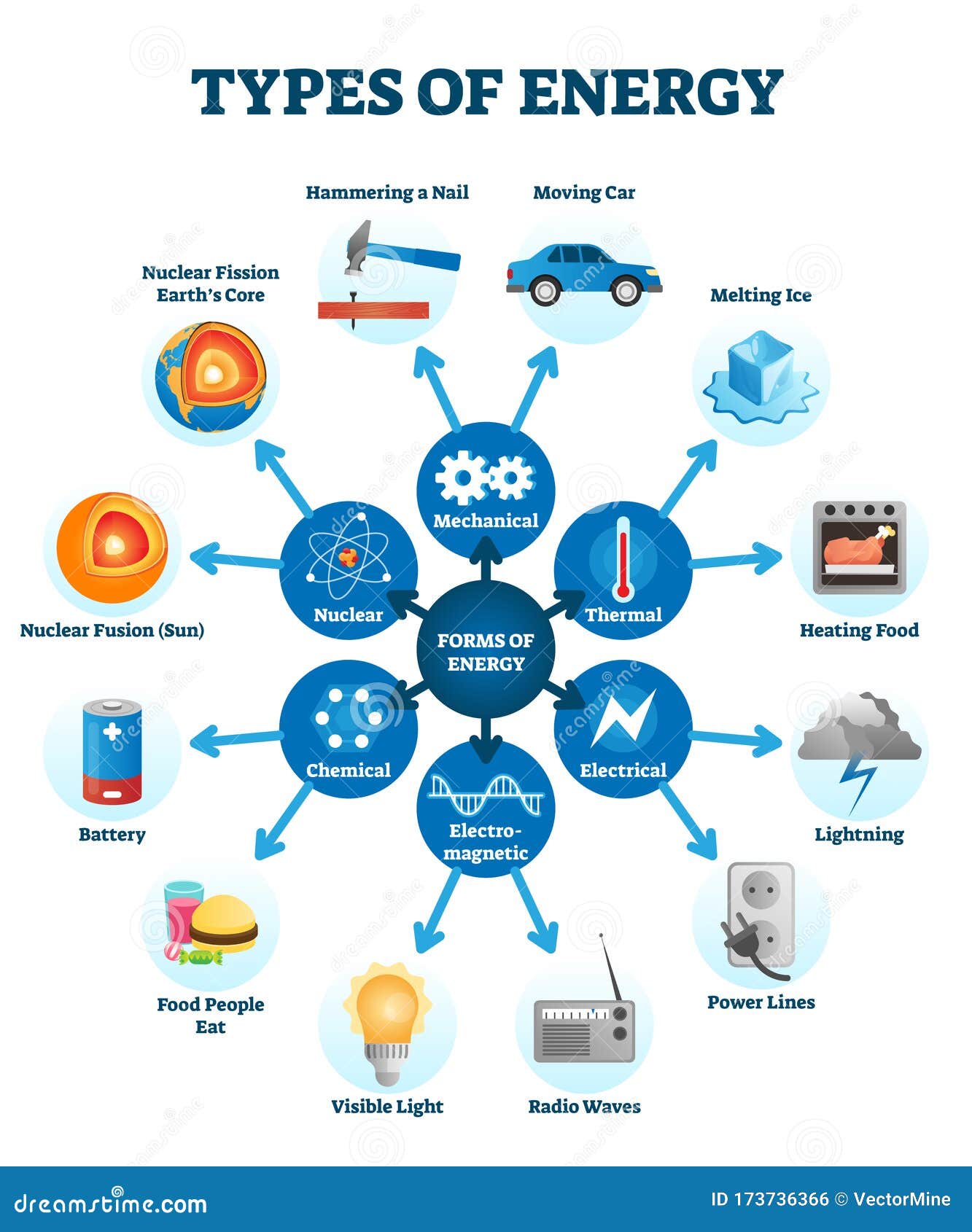
Energy might sound like a simple idea, but it’s a bit more complex than it seems. In scientific terms, energy refers to the capacity to perform work. Work, in this context, means moving something or causing change. Energy can take many shapes, such as potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, and more. These forms aren’t isolated; they often transform into one another depending on the situation.
For example, think about turning on a light. The electrical energy flowing through the bulb converts into light and heat energy. Similarly, when you ride a bike, your body uses chemical energy from food to produce kinetic energy that propels you forward. Energy transformations happen all the time, and they’re what keep the universe humming along.
What Forms Does Energy Take?
Energy shows up in different forms, each serving a specific purpose. Let’s break them down:
- Potential Energy: This is the energy stored in an object based on its position or state. A book sitting on a shelf has potential energy because it could fall if nudged.
- Kinetic Energy: This is the energy of motion. Anything that moves, from a rolling ball to a speeding car, has kinetic energy.
- Chemical Energy: Found in the bonds between atoms and molecules, chemical energy powers everything from our bodies to car engines.
- Thermal Energy: Also known as heat, thermal energy is generated by the movement of particles within matter.
- Electrical Energy: This type of energy flows through wires and powers our gadgets.
Each form of energy has its own unique characteristics, yet they’re all interconnected. That’s why understanding one form can help you grasp others.
What What is Energy - The History
The concept of energy has been around for centuries, with roots tracing back to ancient Greece. The word itself comes from the Greek term "enérgeia," meaning activity. Over time, scientists have expanded our knowledge of energy, uncovering its many forms and applications. Today, energy is a cornerstone of modern science and technology.
In the past, people relied on natural sources like wood and wind for energy. Now, we’ve developed advanced methods to harness energy from the sun, wind, water, and even atoms. These advancements have revolutionized how we live, work, and interact with the world.
How Does Energy Work?
Energy doesn’t just exist; it moves and changes. Think of it like a game of tag where energy passes from one thing to another. For instance, when you strike a match, the chemical energy stored in the stick transforms into heat and light energy. This transfer continues until the energy dissipates or changes form again.
Energy transformations follow certain rules. One of the most important is the law of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only changed from one form to another. This principle explains why energy remains constant in the universe, even as it shifts between forms.
What Happens When Energy Transforms?
Energy transformations occur all the time, often without us noticing. For example:
When you boil water, thermal energy from the stove heats the water, causing it to change into steam. This steam can then be used to generate electricity in power plants. Similarly, when you pedal a bike, your muscles convert chemical energy into kinetic energy, propelling you forward. Each transformation involves a trade-off, with some energy lost as heat or other byproducts.
Understanding these transformations helps us design better systems for generating and using energy efficiently. It’s all about finding ways to minimize waste and maximize usefulness.
What What is Energy - Mechanical Energy
Mechanical energy is a type of energy related to motion. Anything that moves possesses mechanical energy. This includes cars speeding down highways, rivers flowing through valleys, and even people walking down the street. Mechanical energy combines both kinetic and potential energy, making it versatile and widely applicable.
For instance, a roller coaster at the top of a hill has lots of potential energy due to its height. As it descends, this potential energy converts into kinetic energy, creating the thrilling ride we all love. Mechanical energy is everywhere, powering machines, vehicles, and even our own bodies.
Why Do We Need Energy?
Energy is essential for everything we do. Without it, life as we know it wouldn’t exist. From the smallest cells in our bodies to the largest factories, energy drives processes that sustain life and civilization. We use energy to cook food, heat homes, power machines, and travel across the globe.
But energy isn’t just about convenience; it’s also about survival. Plants use sunlight to produce food through photosynthesis, while animals consume plants or other animals to obtain the energy they need. This cycle of energy transfer forms the basis of ecosystems worldwide.
What What is Energy - Renewable vs Nonrenewable
Not all energy sources are created equal. Some, like fossil fuels, are nonrenewable, meaning they take millions of years to form and will eventually run out. Others, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, are renewable, replenishing naturally over short periods.
Renewable energy sources have gained popularity in recent years due to their environmental benefits. They produce little to no pollution and help combat climate change. However, they come with challenges, such as intermittency and storage issues. Balancing these factors is key to ensuring a sustainable energy future.
What What is Energy - Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is a powerful form of energy derived from the interactions of atomic nuclei. It’s produced through processes like fission, where heavy atoms split apart, and fusion, where light atoms combine. Nuclear power plants generate electricity by harnessing the heat produced during fission reactions.
While nuclear energy offers significant advantages, such as low emissions and high efficiency, it also poses risks. Accidents at plants like Chernobyl and Fukushima highlight the importance of safety measures and responsible management. Despite these challenges, nuclear energy remains a critical component of global energy production.
What What is Energy - Final Thoughts
Energy is the backbone of our modern world, driving progress and innovation. By understanding its various forms and functions, we can appreciate its role in shaping our lives. Whether it’s the food we eat, the electricity that powers our homes, or the fuel that moves our vehicles, energy is an integral part of existence.
This article explored the basics of energy, its forms, and how it works. We also touched on its historical significance, transformations, and importance in daily life. As we continue to explore new ways to generate and use energy, one thing remains clear: energy is a force that connects us all.

What Is Energy? Energy Definition and Examples (Science)

Types of energy infographic 12668443 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Types of Energy Vector Illustration Scheme Stock Vector - Illustration